目录
前言
在服务器上安装的各种中间件,一般都需要配置成开机自启动。但是有些中间件的安装过程中并没有提供相关配置开机自启动的说明文档。 今天总结一下 Centos 下配置服务开机自启动的 3 种方式。
一、Centos 上配置开机自启动的几种方式
- 方式一:直接在 / etc/rc.d/rc.local 中添加服务启动命令
- 方式二:通过 chkconfig 配置服务自启动
- 方式三:Centos7 通过 systemctl enble 配置服务自启动
二、实践演示
1、在 / etc/rc.d/rc.local 中添加服务启动命令
/etc/rc.d/rc.local 脚本会在 Centos 系统启动时被自动执行,所以可以把需要开机后执行的命令直接放在这里。
示例:配置开机启动 [apollo]
vi /etc/rc.d/rc.local
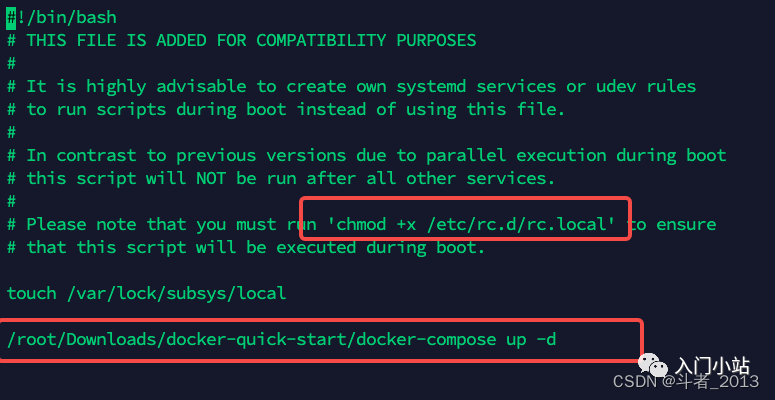
想简单点可以像上面这样直接将服务的启动命令添加到 / etc/rc.d/rc.local 中。
也可以自己编写服务启动的脚本。由于重启时是以 root 用户重启,需要保证 root 用户有脚本执行权限。
1)、编写服务启动的脚本 vi /opt/script/autostart.sh
#!/bin/bash /root/Downloads/docker-quick-start/docker-compose up -d
2)、赋予脚本可执行权限(/opt/script/autostart.sh 是你的脚本路径)
chmod +x /opt/script/autostart.sh
3)、打开 / etc/rc.d/rc.local 文件,在末尾增加如下内容
/opt/script/autostart.sh
3)、在 centos7 中,/etc/rc.d/rc.local 的权限被降低了,所以需要执行如下命令赋予其可执行权限
chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
2、通过 [chkconfig] 配置
在 CentOS7 之前,可以通过 chkconfig 来配置开机自启动服务。 chkconfig 相关命令:
chkconfig –-add xxx //把服务添加到chkconfig列表 chkconfig --del xxx //把服务从chkconfig列表中删除 chkconfig xxx on //开启开机自动启动 chkconfig xxx off //关闭开机自动启动 chkconfig --list //查看所有chklist中服务 chkconfig --list xxx 查看指定服务
chkconfig 运行级别 level 和启动顺序的概念:
chkconfig --list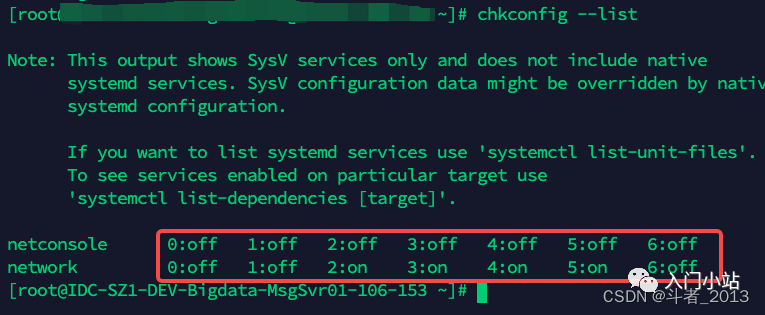 这里的 0 到 6 其实指的就是服务的 level。
这里的 0 到 6 其实指的就是服务的 level。
–level <等级代号> 指定系统服务要在哪一个执行等级中开启或关毕。
等级 0 表示:表示关机 等级 1 表示:单用户模式 等级 2 表示:无网络连接的多用户命令行模式 等级 3 表示:有网络连接的多用户命令行模式 等级 4 表示:不可用 等级 5 表示:带图形界面的多用户模式 等级 6 表示:重新启动
比如如下命令:
//设定mysqld在等级3和5为开机运行服务 chkconfig --level 35 mysqld on //设置network服务开机自启动,会把2~5的等级都设置为on chkconfig network on
表示开机启动配置成功。
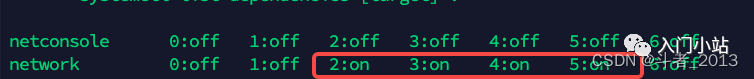
服务的启动顺序又指的什么呢?
服务的启动顺序是指在服务器启动后服务启动脚本执行的顺序。
以系统默认服务 network 说明:
cat /etc/init.d/network
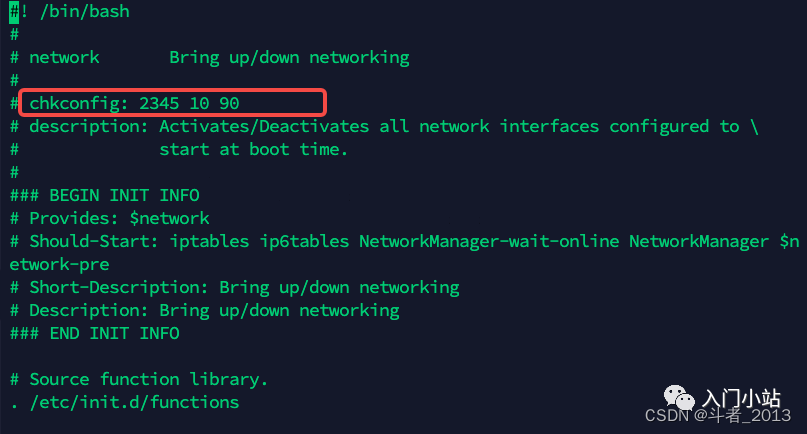
其中
# chkconfig: 2345 10 90用来指定服务在各个 level 下的启动顺序。 该配置的含义是 network 服务在 2、3、4、5 的 level 下的启动顺序是 10,在 1 和 6 的 level 等级下的启动顺序是 90。
chkconfig 配置的服务启动顺序最后都会在/etc/rc.d/目录下体现出来:
cd /etc/rc.d/
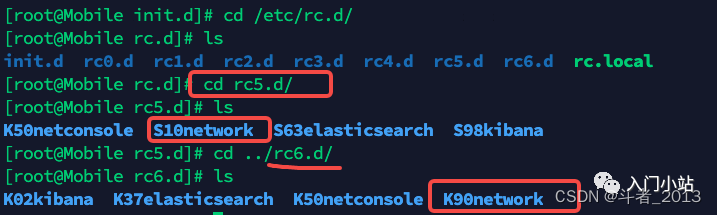
文件中脚本命名规则,首字母K表示关闭脚本,首字母S表示启用脚本,数字表示启动的顺序.
chkconfig 配置实例
通常 [kibana]的官方配置是没有介绍如何配置开机自启动的。这里我配置 kibana 开机自启动来说明。
1、在 / etc/init.d 目录下,新建脚本 kibana
cd /etc/init.d vi kibana
脚本内容如下:
#!/bin/bash # chkconfig: 2345 98 02 # description: kibana KIBANA_HOME=/usr/local/kibana-6.2.4-linux-x86_64 case $1 in start) $KIBANA_HOME/bin/kibana & echo "kibana start" ;; stop) kibana_pid_str=`netstat -tlnp |grep 5601 | awk '{print $7}'` kibana_pid=`echo ${kibana_pid_str%%/*}` kill -9 $kibana_pid echo "kibana stopped" ;; restart) kibana_pid_str=`netstat -tlnp |grep 5601 | awk '{print $7}'` kibana_pid=${kibana_pid_str%%/*} kibana_pid=`echo ${kibana_pid_str%%/*}` kill -9 $kibana_pid echo "kibana stopped" $KIBANA_HOME/bin/kibana & echo "kibana start" ;; status) kibana_pid_str=`netstat -tlnp |grep 5601 | awk '{print $7}'` if test -z $kibana_pid_str; then echo "kibana is stopped" else pid=`echo ${kibana_pid_str%%/*}` echo "kibana is started,pid:"${pid} fi ;; *) echo "start|stop|restart|status" ;; esac
注意⚠️:
每个被 chkconfig 管理的服务需要在对应的 init.d 下的脚本加上两行或者更多行的注释。 第一行告诉 chkconfig 缺省启动的运行级以及启动和停止的优先级。如果某服务缺省不在任何运行级启动,那么使用 - 代替运行级。 第二行对服务进行描述,可以用 \ 跨行注释。
#!/bin/bash #chkconfig:2345 98 02 #description:kibana
解释说明:
配置 kibana 服务在 2、3、4、5 的 level 等级下脚本执行顺序是 98,
1、6 的 level 等级下脚本执行顺序是 01。
2、增加脚本的可执行权限
chmod +x kibana
3、查看 chkconfig list
chkconfig --list
4、把服务添加到 chkconfig 列表
chkconfig --add kibana
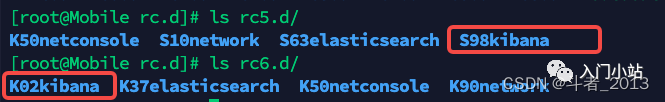
5、设置 kibana 服务自启动
chkconfig kibana on //开启开机自动启动
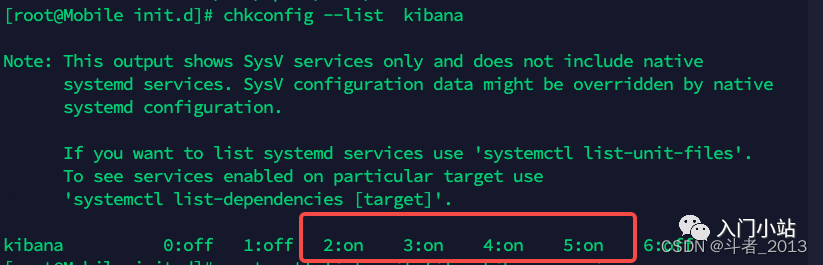
6、查看 kibana 服务自启动状态
chkconfig --list kibana
如果2~5都是on,就表明会自动启动了
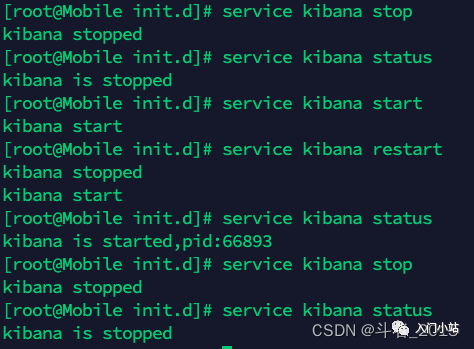
 7、服务的启动、停止、重启和状态查看
7、服务的启动、停止、重启和状态查看
//查看服务状态 service kibana status //服务启动 service kibana start //服务停止 service kibana stop //服务重启 service kibana restart
3、Centos7 通过 systemctl enble 配置服务自启动
在 Centos7 后,更推荐通过
systemctl来控制服务。
| 任务 | 旧指令 | 新指令 |
|---|---|---|
| 使某服务自动启动 | Chkconfig --level 3 httpd on | systemctl enable httpd.service |
| 使某服务不自动启动 | chkconfig --level 3 httpd off | systemctl disable httpd.service |
| 检查服务状态 | service httpd status | systemctl status httpd.service (服务详细信息) systemctl is-active httpd.service(仅显示是否 Active) |
| 显示所有已启动的服务 | chkconfig --list | systemctl list-unit-files systemctl list-units --type=service |
| 启动某服务 | service httpd start | systemctl start httpd.service |
| 停止某服务 | service httpd stop | systemctl stop httpd.service |
| 重启某服务 | service httpd restart | systemctl restart httpd.service |
1、systemctl 服务的目录介绍
知道服务的管理是通过 systemd,而 systemd 的配置文件大部分放置于
/usr/lib/systemd/目录内。但是 Red Hat 官方文件指出, 该目录的文件主要是原本软件所提供的设置,建议不要修改!而要修改的位置应该放置于/etc/systemd/system/目录内。
详情查看:https://wizardforcel.gitbooks.io/vbird-linux-basic-4e/content/150.html
Centos 系统服务脚本目录:
/usr/lib/systemd/
有系统(system)和用户(user)之分,如需要开机没有登陆情况下就能运行的程序,存在系统服务(system)里,即:
/usr/lib/systemd/system/
反之,用户登录后才能运行的程序,存在用户(user)里,服务以. service 结尾。
/usr/lib/systemd/user/
2、建立 kibana 开机服务 1)、建立 kibana 服务文件
cd /etc/systemd/system/ vim kibana.service
脚本内容:
[Unit] Description=kibana After=network.target [Service] Type=forking User=root Group=root ExecStart=/etc/init.d/kibana start ExecReload=/etc/init.d/kibana restart ExecStop=/etc/init.d/kibana stop PrivateTmp=true [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
注意⚠️:
这里
ExecStart、ExecReload、ExecStop的命令还是借助了上文在 / etc/init.d 目录下配置 kibana 脚本来实现。 [Service] 的启动、重启、停止命令全部要求使用绝对路径 [Install] 服务安装的相关设置,可设置为多用户
参数说明: Description: 描述服务 After: 描述服务类别
[Service] 服务运行参数的设置 Type=forking 是后台运行的形式 User 服务启动用户 Group 服务启动用户组 ExecStart 为服务的具体运行命令 ExecReload 为重启命令 ExecStop 为停止命令 PrivateTmp=True 表示给服务分配独立的临时空间
2)、赋予执行权限
chmod 754 kibana.service
依照上面的表格,权限组合就是对应权限值求和,如下: 7 = 4 + 2 + 1 读写运行权限 5 = 4 + 1 读和运行权限 4 = 4 只读权限.
这句命令的意思是将 filename 文件的读写运行权限赋予文件所有者,把读和运行的权限赋予群组用户,把读的权限赋予其他用户。
3)、服务的启动、停止、开机启动
- 查看服务状态
//重新加载某个服务的配置文件,如果新安装了一个服务,归属于 systemctl 管理,要是新服务的服务程序配置文件生效,需重新加载 systemctl daemon-reload //查看服务状态 systemctl status kibana.service
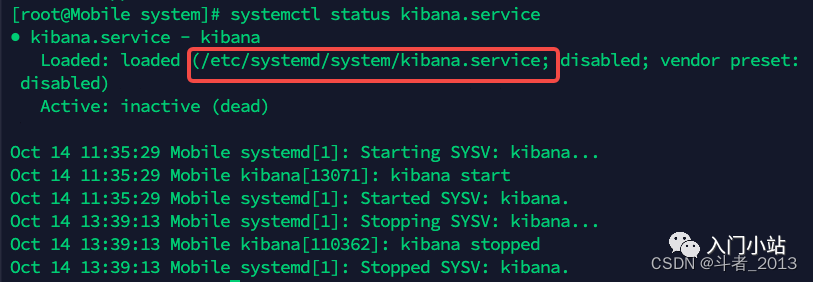
- 启动服务
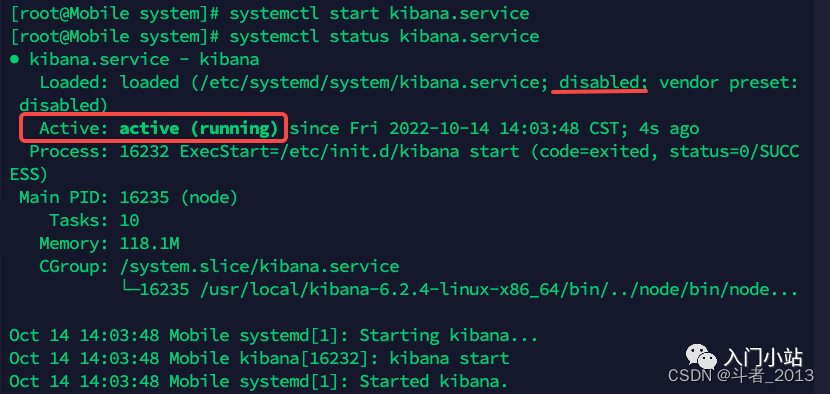
其中,
disabled说明服务还没有开启开机自启动。
- 开启服务开机启动
systemctl enable kibana.service
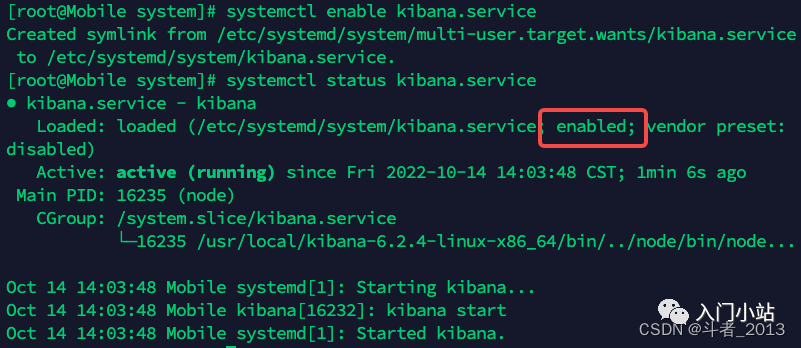
服务状态说明:
systemctl status 服务名称
| 状态 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| loaded | 系统服务已经初始化完成,加载过配置 |
| active(running) | 正有一个或多个程序正在系统中执行, vsftpd 就是这种模式 |
| atcive(exited) | 僅執行一次就正常結束的服務, 目前並沒有任何程序在系統中執行 |
| atcive(waiting) | 正在執行當中,不過還再等待其他的事件才能继续处理 |
| inactive | 服务关闭 |
| enbaled | 服务开机启动 |
| disabled | 服务开机不自启 |
| static | 服务开机启动项不可被管理 |
| failed | 系统配置错误 |
常用服务文件 1.nginx.service
[Unit] Description=nginx - high performance web server After=network.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target [Service] Type=forking ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf ExecReload=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload ExecStop=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
2.mysql.service
[Unit] Description=mysql After=network.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target [Service] Type=forking ExecStart=/usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server start #ExecReload=/usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server restart #ExecStop=/usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server stop #PrivateTmp=true [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
4.redis.service
[Unit] Description=Redis After=network.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target [Service] Type=forking ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/redis-server /etc/redis.conf ExecStop=kill -INT `cat /tmp/redis.pid` User=www Group=www [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
5.supervisord.service
[Unit] Description=Process Monitoring and Control Daemon After=rc-local.service [Service] Type=forking ExecStart=/usr/bin/supervisord -c /etc/supervisord.conf SysVStartPriority=99 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
总结
本文主要总结了 Centos 上配置开机自启动的 3 种方式
- 方式一:直接在 / etc/rc.d/rc.local 中添加服务启动命令
- 方式二:通过 chkconfig 配置服务自启动
- 方式三:Centos7 通过 systemctl enble 配置服务开机自启动


本文作者:Gustav
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
